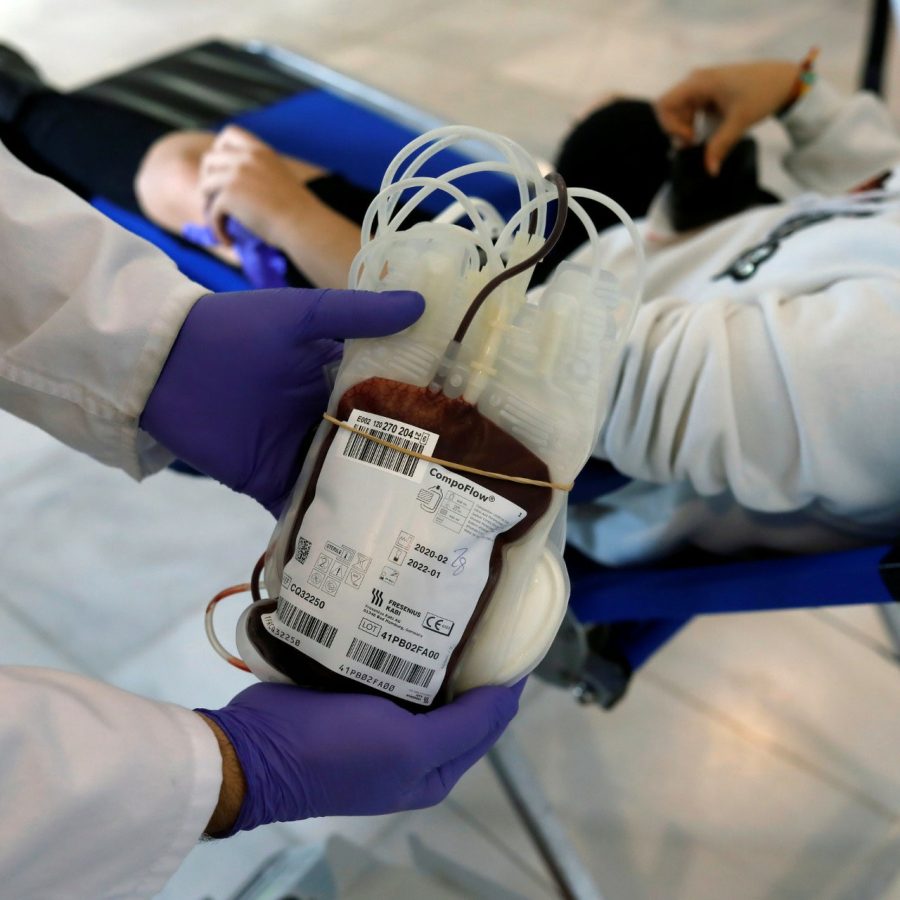
Despite lockdown measures being in
place to curb the spread of SARS-
CoV-2, it is crucial that people still donate blood.
Donating blood is all the more important during the pandemic. Covid-19’s sudden emergence and rapid spread across the world have fundamentally changed how societies function, requiring radical restrictions on movement.
These lockdowns aim to limit the transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to reduce both the number of people dying after becoming infected and the strain on overloaded intensive care units.
As well as these key workers, other people who are crucial for maintaining the health of a population are those who donate blood. Depending on the reason why a person needs a blood transfusion, theNHLBI highlight that it is possible to give four different types of blood product during transfusion: whole blood, red blood cells, platelets, or plasma.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), blood transfusions are lifesaving procedures that occur every day in hospitals across the United States. There are more than 13.2 million blood donors in the U.S., who are crucial for the country’s blood supply. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) point out that someone needs a blood transfusion every 2 seconds.
LONELINESS LIKELY TO DECREASE WITH AGE, STUDY FINDS: A new study has suggested that loneliness decreases with age. In addition, it seems to be less prevalent in collectivist societies than in individualistic ones and less common in women than in men. New research suggests that men are more likely than women to feel lonely.
New research suggests that young people are more likely than older people to feel lonely, that people in countries that are collectivist rather than individualistic are less likely to feel lonely, and that loneliness is more likely to affect men than women.
The authors of the present study state that loneliness can be understood as “the discrepancy between actual and desired social relationships.”
According to this definition, two people who have the same number of social relationships may experience loneliness differently if one desires more social relationships than the other.
While researchers know that many other factors can affect loneliness, few studies have been large or diverse enough to get an accurate picture as to what these may be and how they might interact.
The study drew on the BBC’s Loneliness Experiment dataset. This dataset contains information from nearly 55,000 people aged between 16 and 99 from 237 countries, islands, and territories, making it one of the largest and most diverse of its kind.