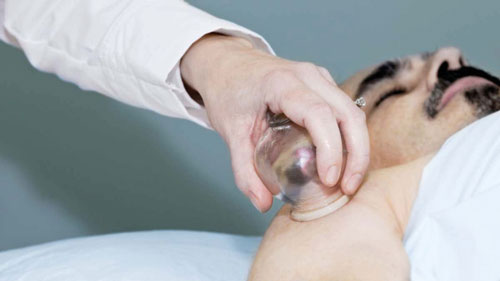
A team of researchers recently developed a novel way of delivering nucleic acid-based medicines using a method similar to an ancient cupping technique.
Their experiments indicate that the technique makes vaccine delivery more effective by several orders of magnitude.
The cupping technique is currently undergoing clinical trials to deliver a COVID-19 vaccine.
Over the past 20 years, scientists have developed a range of nucleic acid-based medicines as both treatmentsTrusted Source and vaccinesTrusted Source.
Nucleic acids are present in all living cells, most notably as DNA and RNA. Treatments and vaccines that use nucleic acids work by inhibiting, adding, replacing, or editing DNA and RNA in host cells.
How well these treatments and vaccines work depends on how well they can be delivered to the host’s cells. If directly injected into tissue, for example, most nucleic acids will rapidly degrade unless protected.
The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines are both nucleic acid-based medicines. Nucleic acids in these vaccines are enclosed and protected by lipid nanoparticles that deliver them across the host cell membrane.
Although they are effective, drugs delivered in this way are vulnerable to degradationTrusted Source during storage.
One delivery method for nucleic acid-based medicines is electroporationTrusted Source. This involves delivering nucleic acids to cells made more permeable using a pulse of electricity.
While somewhat effective, these electrical impulses can cause muscle contractions, tissue damage, and pain, and they may not be suitable for people who use implantable electrical devices such as defibrillators or pacemakers.
Using this method also requires substantial training, and equipment costs may make it inaccessible to regions and populations with fewer resources.