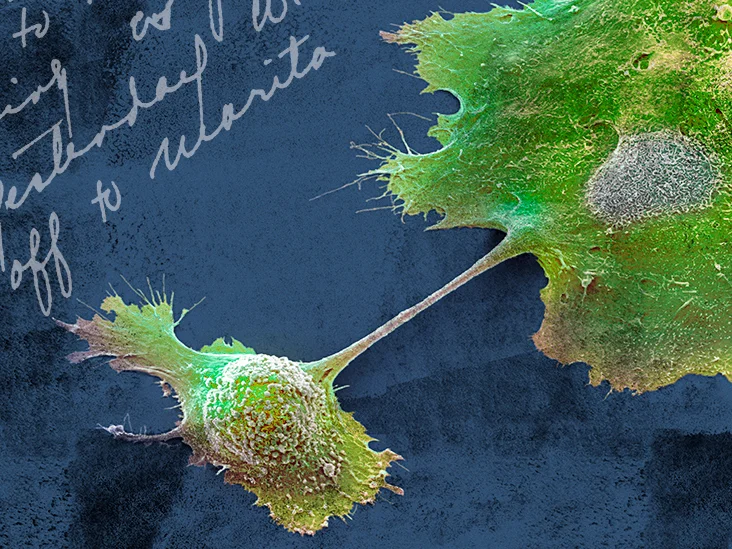
Cancer causes cells to divide uncontrollably. This can result in tumors, damage to the immune system, and other impairment that can be fatal. Cancer can affect various parts of the body, such as the breasts, lungs, prostate, and skin. In the United States, an estimated 15.5 millionTrusted Source people with a history of cancer were living as of January 1, 2016, according to a 2018 report from the American Cancer Society.
In this article, we examine types of cancer, how the disease develops, and the many treatments that help improve the quality of life and survival rates. Photo edited by Stephen Kelly; Science Photo Library – STEVE GSCHMEISSNER/ CSA Images/Getty Images
Cancer is a broad term. It describes the disease that results when cellular changes cause the uncontrolled growth and division of cells.
Some types of cancer cause rapid cell growth, while others cause cells to grow and divide at a slower rate.
Certain forms of cancer result in visible growths called tumors, while others, such as leukemia, do not.
Most of the body’s cells have specific functions and fixed lifespans. While it may sound like a bad thing, cell death is part of a natural and beneficial phenomenon called apoptosis. A cell receives instructions to die so that the body can replace it with a newer cell that functions better. Cancerous cells lack the components that instruct them to stop dividing and to die. As a result, they build up in the body, using oxygen and nutrients that would usually nourish other cells. Cancerous cells can form tumors, impair the immune system and cause other changes that prevent the body from functioning regularly.
Cancerous cells may appear in one area, then spread via the lymph nodes. These are clusters of immune cells located throughout the body.
For example, over 480,000 peopleTrusted Source die in the U.S. each year from smoking cigarettes, according to data reported in 2014.
Other causes of cancer are not preventable. Currently, the most significant unpreventable risk factor is age. According to the American Cancer Society, doctors in the U.S. diagnose 87 percentTrusted Source of cancer cases in people ages 50 years or older. Genetic factors can contribute to the development of cancer.
A person’s genetic code tells their cells when to divide and expire. Changes in the genes can lead to faulty instructions, and cancer can result.