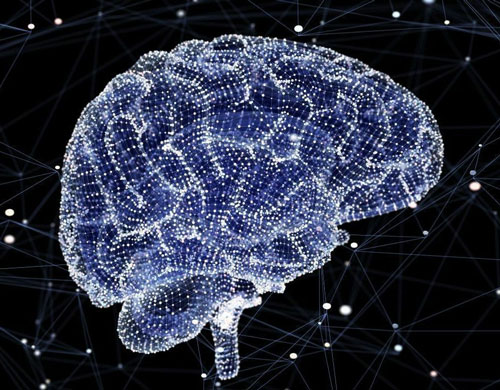
A new study reveals how neurons in the gut wall relay sensory information to the spinal cord and brain, which may influence mood and well-being.
The enteric nervous system (ENS) sometimes referred to as the “second brain” is the nervous system of the gut.
It contains some 500 million neurons and controls important reflexes, such as peristalsis, the contraction of muscles in the gut to enable digestion. It is also responsible for the secretion of digestive enzymes that help break down food.
The ENS is also a critical part of the gut-brain axis, through which the gut communicates with the brain — and the vagus nerve is particularly essential for conveying information about the intestines to the brain.
The gut-brain axis performs several functions. The majority of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood, is found in the gut, for example.
In a new study, in Adelaide, Australia, have identified a new way that neurons in the gut wall can activate neurons that connect to those in the spinal cord.
The researchers recorded the electrical activity of the viscerofugal neurons. They found that the firing of these neurons was associated with changes in the activity of the smooth muscle of the colon.
“The new study has uncovered how viscerofugal neurons provide a pathway so our gut can ‘sense’ what is going on inside the gut wall, then relay this sensory information more dynamically than was previously assumed to other organs, like the spinal cord and brain, which influence our decisions, mood and general well-being,” explains Prof. Spencer.
LUCID DREAMING STUDY EXPLAINS HOW TO TAKE CONTROL OF OUR DREAMS
The largest study on lucid dreaming to date has identified the best techniques to help people take control of their nightly dreams. This practice could help people in their daily lives.
Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon in which a person is aware that they are asleep and dreaming.
Those who are more adept at lucid dreaming are able to control the action and content of their dreams to varying degrees.
But can people learn to lucid dream and perfect their technique? the answer is “yes.” currently a visiting fellow tested the effectiveness of five different techniques in achieving lucid dreaming.
Aspy has been fascinated by lucid dreaming for many years, and in a comment , he explained how this fascination came about.